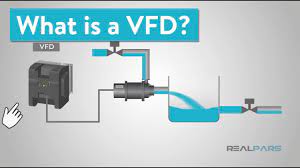
In this article, we will learn about VFD and its applications. We will also cover in detail the converter and the DC link. Finally, we will cover the IGBT module, and how PWM allows for AC output to the motor for precise motor speed control.
AC motor rotational speed
Induction or alternating current electric motors rotate at a rate that is set by the number of poles inside the motor itself, and the power supplied.
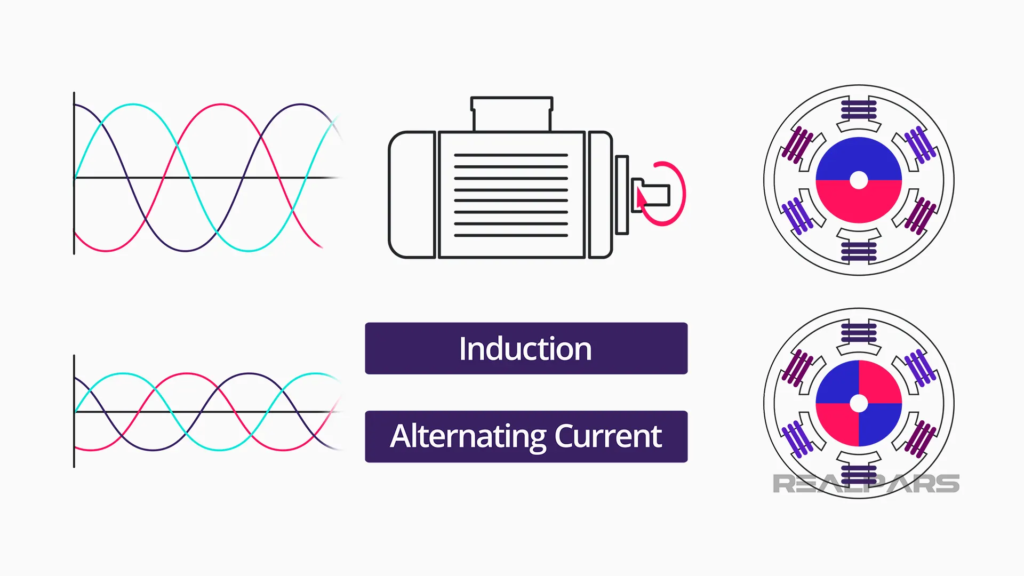
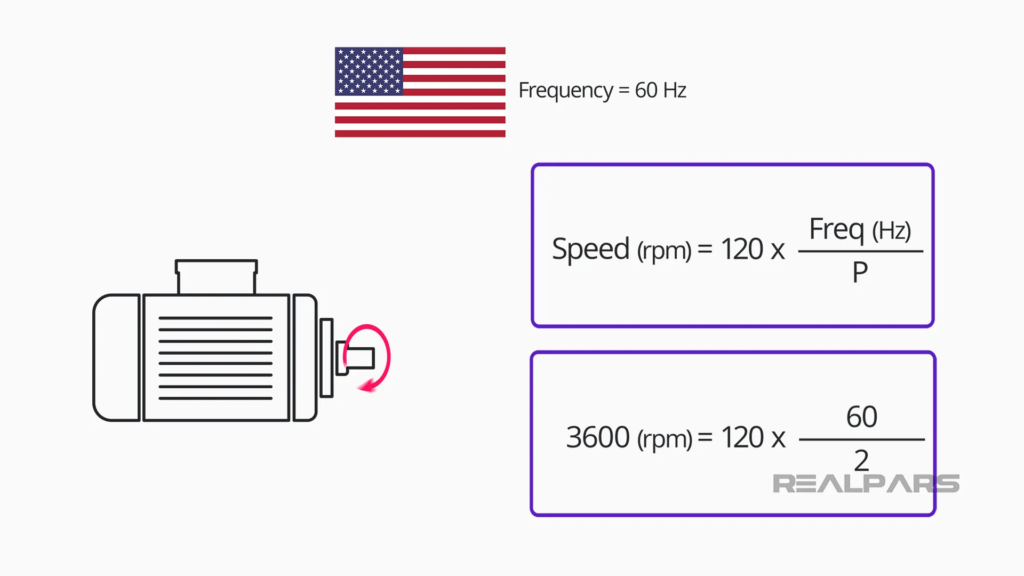
The frequency (measured in Hertz) is directly related to the Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) of a motor. The higher the frequency, the faster the RPM or the higher the engine rotation speed.
In the United States, electric power utilities provide alternating energy with a frequency of 60Hz. A standard two-pole AC motor operating at this frequency provides a nominal rotation of 3600 RPM.
Speed reduction
If an application does not require an electric motor running at full speed of 3600 RPM, which is very common, a few solutions exist:
1: Using a mechanical speed reducer
It mechanically decreases the output speed by increasing torque – the output gear has more teeth than the input gear.